IF SAUDI ARAMCO is a state within a state in Saudi Arabia, then the blandly named Oil Supply Planning and Scheduling (OSPAS) is its deep state. To enter it, you pass tight security at Aramco’s suburban-style headquarters in Dhahran, in the east of the kingdom. The transition is eye-opening. Suddenly, English is the common tongue even among Saudi “Aramcons”, as its workers are known. Female employees, their faces uncovered, lead meetings of male colleagues. The crisp banter is common to engineers everywhere. A toilet break is called a “pressure-relief” exercise.
Deep within, OSPAS is even further removed from the kingdom outside. The few executives with clearance to enter call it the “nerve centre” of the world’s largest oil company. Using 100,000 sensors and data points on wells, pipelines, plants and terminals, it directs every drop of oil and cubic foot of gas that comes out of the kingdom (10% of the world’s oil supply), monitors it on giant screens as it heads to ports and power stations, and tracks oil tankers as they load. Well managers in the desert outback wait daily for OSPAS to tell them what to do. “It’s not just pretty graphics,” an executive says, purring appreciatively over the 70-metre web of data flashing on the wall.
-
Retail sales, producer prices, wages and exchange rates
-
Foreign reserves
-
How taxes can align the interests of individuals and society
-
The case against shrinking the Fed’s balance-sheet
-
Can companies block employees’ class-action lawsuits?
-
Kenya’s supreme court explains why it annulled last month’s presidential poll
Because Aramco has all its “upstream” oil-and-gas operations in one country, it says it can justify investing big sums—and a lot of computer capacity—on such technology, because it helps cut costs. “ExxonMobil operates in 40-plus countries. It just can’t do that,” the executive adds, before apologising lest he appear to bad-mouth a client and partner, one of Aramco’s American founding former shareholders.
Such comparisons will become more pertinent as Aramco opens itself up for an initial public offering (IPO). Until recently it was just as cloistered from outside scrutiny as the kingdom itself, giving it more of a mystique than a good reputation. This week it invited The Economist for a visit. It only partially lifted its veil; its finances remain off-limits to everyone except the government, its only shareholder. Affable executives dodge almost every attempt to wheedle out useful ways of comparing the firm with its listed peers (it has no peers, they dissemble).
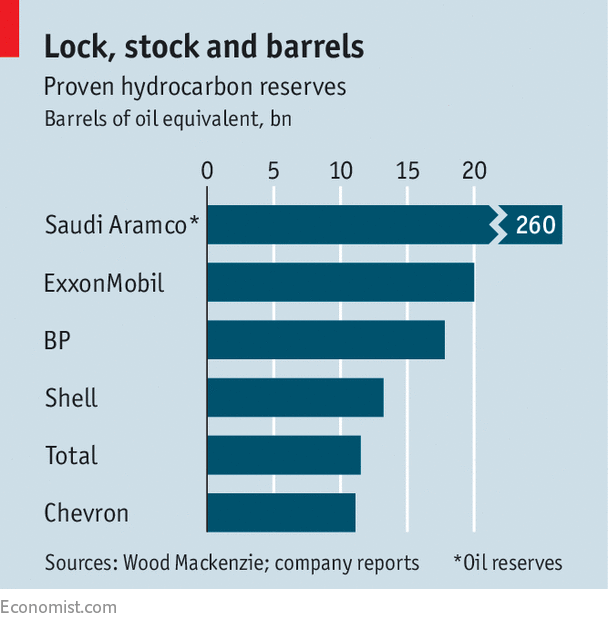
But despite the hermeticism, Aramco has a good tale to tell. Even as its rivals have retrenched owing to low prices, it has stuck to long-term plans, investing heavily in technology, training and the future of oil. Its long-term approach may help explain one mystery. For decades, Saudi Arabia’s declared oil reserves have confounded the industry; since 1989 they have remained suspiciously constant at around 260bn barrels—a dozen times those of Aramco’s nearest listed rival (see chart). As if to rub it in, Aramco says the kingdom has a whopping 400bn further barrels of resources that could one day become reserves.
These reserves are under audit ahead of the IPO, and executives are loth to discuss the process. However, they argue that whereas other companies have to go far to find new reserves, Aramco can keep them constant simply by better stewardship of its existing fields. Amin Nasser, the chief executive, says the company’s recovery rates—the share of oil recouped from what is available in a field—average about 50%, but rise as high as 70%, compared with a global average of about 33%. It does this by maintaining the pressure of its wells over the long term through gas re-injection and other means. Raising recovery rates on average to 70% would add 80bn barrels to reserves, an executive says. That is four times ExxonMobil’s latest total.
Unlike big listed companies, which scrapped growth plans when the price of oil slumped in 2014-16, Aramco has also been able to keep on investing because of its low costs, Mr Nasser says. Increasing natural-gas output is now the main focus, but it has also raised oil production in some areas. This is visible at the vast Shaybah field in Saudi Arabia’s blisteringly hot Empty Quarter, where Aramco last year upped oil output by 250,000 barrels a day (b/d) to 1m b/d, inaugurated a facility to process natural-gas liquids (pictured on previous page) and laid 650km of new pipelines across a mountain range of red sand dunes. (Aramco also set out to repopulate the surrounding desert with oryx, gazelle and ostrich hunted almost to extinction. They are now reproducing, although the first ostrich eggs to fertilise sadly cooked in the heat.)
Its second focus is technology. Whereas some of its peers admit that they squandered the chance to invest in big data during the oil boom before 2014, Aramco has no such regrets. Last year it inaugurated its home-grown “TeraPowers” technology, which uses 1trn pixel-like computational cells to simulate the flow of hydrocarbons through 500m years of geological time, enabling it to model oilfields in granular detail. From Dhahran it can remotely direct drilling of horizontal wells in Shaybah, steering a drill-bit through miles of rock to within a few feet of its target. (Royal Dutch Shell recently boasted of using similar remote-drilling technology in Argentina.) To train young employees in understanding the subsurface, Aramco has a 3D virtual-reality “cave” in Dhahran, which shows the filigree of wells 1,500 metres below the surface of Shaybah, as if from a submarine.
Third, as Saudi Arabia’s most attractive employer, Aramco has less difficulty than its Western peers in attracting millennial recruits (born between around 1980 and 1996) who are turning away from the oil and gas industry. It has kept up spending on international scholarships during the slump. It plans to raise the share of women in the workforce from 25% to 40%. Its chief engineer and head of human resources are both female. Saudi labour laws still apply, however: female Aramcons may not stay overnight at an oilfield.
Aramcons pride themselves on a Westernised culture handed down from their American forefathers before nationalisation in 1980. This makes them confident they can handle the listing. “From the way [Aramco] was built, from the beginning I would say it was ready for an IPO,” Mr Nasser says. The main change, he adds, will be issuing quarterly results.
But that underplays the challenges ahead. For one thing, Aramco is not master of its destiny. The future of the IPO, such as the decision on where and when to list, is in the hands of the government shareholder, represented by Muhammad bin Salman, the crown prince. Domestic political tension and external frictions with Qatar risk delaying the IPO until 2019—and further muddying the waters.
The potential valuation is also contentious. MBS, as the crown prince is known, has said he believes Aramco is worth $2trn, though many analysts think that is over-ambitious. To improve its chances, the kingdom is leaning toward a listing on the New York Stock Exchange rather than in London, because America has deeper pools of capital. However, that would expose Aramco to legal risks it would prefer to avoid. In order to bring in Chinese investors, the kingdom is also considering issuing some shares in Hong Kong.
However strong Aramco may be upstream, its lower-margin refining and petrochemicals divisions will drag down the valuation. Aramco has some intriguing plans to mitigate this, hoping in the next few years to build a plant with new technology to turn crude oil directly into petrochemicals—in essence, leap-frogging refineries. But this is untested.
In sum, the IPO is more for the kingdom’s benefit than Aramco’s. It could have drawbacks—exposing the firm to investors with short time horizons or to activists hostile to fossil fuels. But the Aramcons appear determined to make the most of it. Executives argue that oil’s future is bright, even if electric cars and cleaner fuels emerge. Low costs mean there is no danger Saudi oil will become a “sunset industry”, says Mohammed al-Qahtani, head of its upstream division. A listing will make Aramco “the envy of the rest of the world”.
Source: economist
Behind the veil of Saudi Aramco