THE proposed sale of 5% of Saudi Aramco is not just likely to be the biggest initial public offering (IPO) of all time. “It’s like Gibraltar selling the rock,” as one expert on Saudi Arabia’s oil policy puts it. The world’s biggest oil company keeps the House of Saud in power, bankrolled 60% of the national budget last year, and is a paragon of efficiency in an economy otherwise mired in bureaucracy.
The elevation on June 21st of Muhammad bin Salman, the 31-year-old architect of the IPO, to crown prince is likely to add more momentum to a sale planned for the second half of 2018. The news will further sideline domestic critics of the IPO, some of whom wonder whether it would be better to borrow the money than sell the family silver. But the success of the IPO is not guaranteed. The tendency of MBS, as the prince is known, to micromanage the listing runs counter to the spirit of openness and liberalisation that he says he wants for Saudi Arabia. That could backfire on the IPO itself. The more he interferes, the less keen investors will be to buy shares.
-
Retail sales, producer prices, wages and exchange rates
-
Foreign reserves
-
How the euro zone deals with failing banks
-
The Supreme Court says offensive trademarks are protected speech
-
The hope for Democrats after special-election losses
-
Disappointment for the Democrats in a fiercely fought congressional race
Aramco’s role underpinning the Saudi economy is an even bigger challenge in valuing this IPO than the firm’s immense size. On the one hand, advisers say, its low costs and lean workforce make it comparable to blue-chip oil supermajors such as ExxonMobil and Royal Dutch Shell. On the other, the risks of political interference mean that it is likely to suffer from the stigma associated with being a national oil company (NOC). Many NOCs, such as PetroChina and Brazil’s Petrobras, have come to market amid the sort of fanfare that Aramco is generating. In a decade, they have destroyed more than $500bn-worth of value compared with their private peers (see chart).
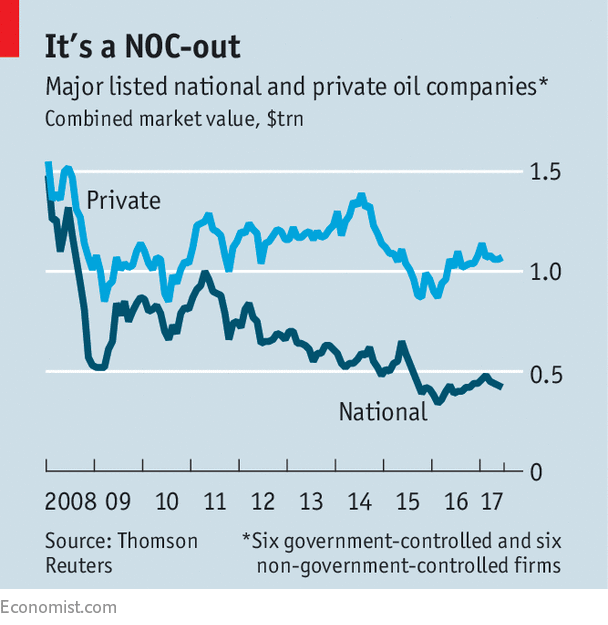
As an oil company, the selling-points for Aramco are strong (provided the oil price is high enough). It has a concession for 12 times more oil and gas than ExxonMobil and 27 times more than Shell. Its production levels are several times higher. It has fewer employees, higher debt-adjusted cashflow per barrel, and decent margins in its refining and petrochemicals businesses as well as upstream. By the time it lists, its advisers hope it will have a board structure similar to that of the supermajors, and will be comparable on a number of parameters, including dividend projections, that will enable investors to value it accordingly. “The day this company goes public, it will look like one of the top blue-chip oil companies,” one says.
The trouble is, MBS has already stated what he thinks the valuation should be, and at $2trn, it is punchy enough to make even a Silicon Valley boss look bashful. To achieve it, a 5% sliver would be worth $100bn—four times the biggest IPO to date, that of China’s Alibaba, an e-commerce firm, in 2014.
According to an analysis by Sanford C. Bernstein, a research firm, at $2trn its value per barrel of oil equivalent coming out of the ground would be about 60% higher than that of its blue-chip peers. A valuation at or below $1.5trn would be closer to the mark, but risks disappointing the new crown prince. “He may have to make a choice between selling cheap and pulling the plug on the process. Either case would be a loss of face,” says Steffen Hertog of the London School of Economics, a writer on the state and oil in Saudi Arabia.
To get closer to his target, the kingdom recently slashed tax rates on Aramco, from 85% to 50%. That brings them nearer to international norms for oil firms and will appeal to investors: lower taxes mean the company can pay out higher dividends.
The country also has a plan to wean its people off some of the world’s cheapest energy by 2020, which would bolster Aramco’s profits. According to Jim Krane, of Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy, about a third of Aramco’s output is sold for domestic purposes, with power generation, for instance, enjoying discounted prices of under $6 a barrel—a “massive opportunity cost”.
But investors would be wise not to view issues like taxes and subsidies in isolation. Some analysts express worry that dividends are unstable, and that the kingdom would have to unwind the tax cuts on Aramco if the state needed the money. The introduction of more realistic pricing could also have political and social ramifications, since Saudis are some of the world’s biggest consumers of cheap energy.
Another worry for investors would be if MBS continues to use Aramco as a tool of global oil policy on behalf of OPEC, the producers’ cartel. The kingdom may believe that OPEC serves as a stabilising force in global oil markets, which benefits Aramco. But its latest attempts to play puppet-master with the oil market have been counter-productive. On June 21st global oil prices fell to their lowest level since August, despite an agreement by OPEC and non-OPEC producers to cut output until next March. As a result, Aramco is not only losing income, it is losing market share to rivals not bound by the cuts.
Last, as his global stature grows, the prince may be tempted to mix up geopolitics and commerce. Anecdotal evidence of this emerged during President Donald Trump’s visit to Riyadh in May. Even as Aramco was supposedly disentangling itself from the myriad noncore activities it carries out on behalf of the state, the firm was on extra-curricular duty. At breakneck pace, it built the Global Centre for Combating Extremist Ideology in Riyadh, where Mr Trump and MBS’s 81-year-old father, King Salman bin Abdel Aziz Al Saud, performed a weird inauguration ceremony involving a glowing globe. The reason for Aramco’s involvement: no other body in the kingdom could do it half as quickly.
Venue, vidi, vici
Such strategic considerations may also be influencing the decision on whether to list the non-Saudi portion of the IPO in New York or London (a small slice will be listed on Tadawul, the local bourse). Aramco’s lawyers are more comfortable with a London Stock Exchange (LSE) listing, on the ground that it would spare the company the real risk of class-action lawsuits related, for instance, to the terror attacks of September 11th 2001, of litigation from tree-hugging attorneys-general, and of other claims on its assets that it might face on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
But MBS is believed to be leaning more towards New York. This may be because of liquidity: listed companies on the NYSE have a combined market capitalisation of about $20trn, versus $4trn on the LSE. The NYSE also has more prestige; the big peers Aramco wants to be judged against are listed there. Yet he is also understood to have been under pressure from the White House for a New York listing, and is keen to cement ties with Mr Trump. If that were to sway the final consideration, investors might not thank him for it.
Many will shrug. The chance to buy shares in one of the world’s most resilient oil firms will be hard to resist. Moreover, sovereign-wealth funds may well be keen to become “anchor tenants” of the IPO, to deepen their own countries’ relationships with Aramco and the new crown prince.
But MBS’s leapfrog towards the throne will not silence the questions that still swirl. What will happen to the money raised? Will the listing plug a budget gap of 8% of GDP? Will it fund domestic industries such as mining, defence and tourism? Or will it become a “magic money tree”, promising all things to all people? The original goal of the IPO was to bring more transparency and stronger market forces to Saudi Arabia—creating a sort of Thatcherite oasis in the Arabian desert. If that is truly what MBS wants, he should learn to leave well alone.
Source: economist
The prospects for the world’s biggest IPO